Intrauterine Device (IUD): Birth Control, Use & Side Effects
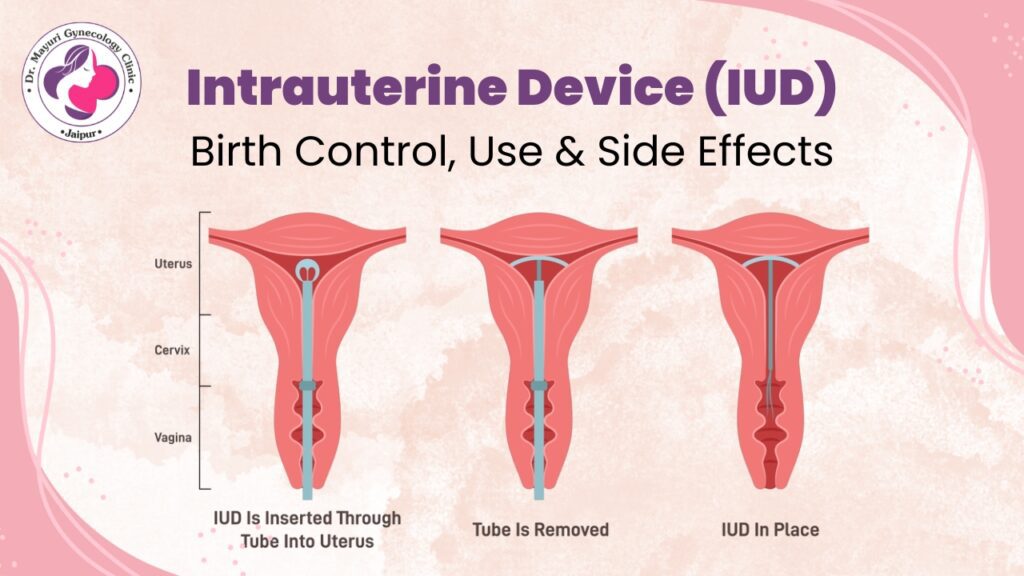
One of the most effective and long-term contraceptive solutions available is the Intrauterine Device (IUD), a small, flexible tool placed inside the uterus by a trained healthcare professional. IUDs are highly effective, easy to use, and reversible, making them a preferred option for many women who want a safe and hassle-free contraceptive method.
This guide explains everything you need to know about IUDs—how they work, the different types, their uses, benefits, side effects, and precautions. The information is designed to be clear and practical, especially for women who are exploring birth control options for the first time.
What is an Intrauterine Device (IUD)?
An IUD is a small, T-shaped device composed of copper or plastic, inserted into the uterus by a medical expert to prevent pregnancy by disrupting the fertilization process. Depending on its type, it may release copper or a small dose of hormones to prevent pregnancy.
The two main types of IUDs include:
- Copper IUD (Non-hormonal)
- Hormonal IUD (Progestin-based)
Both types are highly effective, but they work differently and offer various benefits suited to different needs.
Types of IUDs and How They Work
1. Copper IUD (Non-hormonal)
- How it works: It emits copper ions into the uterus, creating an environment unsuitable for sperm. It blocks sperm from reaching the egg and may also alter the uterine lining, preventing implantation of a fertilized egg.
- Duration: Typically provides protection for 5 to 10 years.
- Best for: Women who prefer a hormone-free option or cannot tolerate hormonal birth control.
- Common brands: Cu-T 380A, Multi-load Cu375.
2. Hormonal IUD
- How it works: A small device that gradually releases progestin (levonorgestrel) inside the uterus, thickening cervical mucus to prevent sperm from entering. In some women, it also stops ovulation, further reducing the chance of pregnancy.
- Duration: The IUD is effective for 3 to 8 years depending on the brand used.
- Additional benefits: Helps reduce heavy menstrual bleeding and painful periods.
- Common brands: Mirena, Skyla, Kyleena, Liletta.
How Do IUDs Prevent Pregnancy?
IUDs prevent pregnancy in one or more of the following ways:
- Thickening cervical mucus – Blocks sperm from entering the uterus.
- Stopping ovulation – Some hormonal IUDs prevent the release of eggs.
- Repelling or killing sperm – Copper IUDs repel or kill sperm by creating a hostile environment where sperm cannot survive.
- Altering the uterine lining – Prevents implantation of a fertilized egg.
Uses of IUDs
Besides preventing pregnancy, IUDs provide additional health and convenience benefits.
1. Reliable Contraception
- It is over 99% reliable in preventing pregnancy.
- Provides long-term protection without needing daily medication.
- Fertility returns immediately after removal.
2. Emergency Contraception
- Copper IUDs can also serve as emergency contraception when used within five days of unprotected intercourse.
- Provides ongoing protection after emergency use.
3. Management of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Hormonal IUDs reduce menstrual flow by thinning the uterine lining.
- Beneficial for women with menorrhagia (heavy periods).
4. Relief from Endometriosis and Pelvic Pain
- Hormonal IUDs reduce inflammation and pain by suppressing menstrual cycles.
5. Possible Protection Against Certain Cancers
- Research suggests hormonal IUDs may lower the risk of endometrial and ovarian cancers by keeping the uterine lining stable.
6. Lower Risk of Pelvic Infections
- Modern IUDs do not increase the risk of infection long-term.
- Hormonal IUDs may reduce infection by thickening cervical mucus.
Advantages of Using an IUD
- Extremely effective: Less than 1% failure rate.
- Long-lasting: Offers up to 10 years of protection with one insertion.
- Reversible: Fertility returns quickly once it’s removed.
- Low maintenance: No need to remember daily medication.
- Discreet: No external signs or need for frequent doctor visits.
- Non-hormonal option: Copper IUDs provide contraception without the use of hormones.
- Cost-effective: One-time cost covers several years of contraception.
Common Side Effects of IUDs
Although safe, some women may experience side effects during the initial months after insertion.
1. Menstrual Changes
- Hormonal IUDs may cause lighter or absent periods.
- Copper IUDs may lead to heavier, longer, and more painful periods.
2. Cramping and Discomfort
- Period-like cramps may occur, especially after insertion.
3. Spotting or Irregular Bleeding
- Some women experience spotting between periods during the initial months.
4. Hormonal Reactions
- Headaches, breast tenderness, acne, mood swings, or ovarian cysts may occur with hormonal IUDs.
5. Expulsion or Misplacement
- Rarely, the device may shift or be expelled, requiring medical attention.
6. Infection Risk
- A small risk of pelvic infection exists shortly after insertion but is rare with proper care.
7. Ectopic Pregnancy
- While unlikely, pregnancy may occur outside the uterus in rare cases.
Conclusion
An IUD is a safe, efficient, and convenient birth control option suitable for many women. Whether you choose a hormone-free copper IUD or a hormonal option like Mirena, both offer long-term protection and additional health benefits.
Talk to a gynecologist or healthcare professional to find out which option suits your personal health and lifestyle best. With professional guidance, proper care, and awareness, IUDs can be a trusted and empowering choice for managing reproductive health.


